USENIX Security '19 - Why Do Adversarial Attacks Transfer? Explaining Transferability of
Attacking machine learning for fun and profit (conversation with the authors of SecML)Подробнее

USENIX Security '19 - Why Do Adversarial Attacks Transfer? Explaining Transferability ofПодробнее

USENIX Security '22 - Transferring Adversarial Robustness Through Robust Representation MatchingПодробнее

USENIX Security '19 - Misleading Authorship Attribution of Source Code using Adversarial LearningПодробнее

USENIX Security '20 - Devil’s Whisper: A General Approach for Physical Adversarial AttacksПодробнее

USENIX Security '19 - Lessons Learned from Evaluating the Robustness of Defenses toПодробнее

USENIX Security '18 - When Does Machine Learning FAIL?...Подробнее

USENIX Security '24 - Transferability of White-box Perturbations: Query-Efficient Adversarial...Подробнее

USENIX Security '19 - Understanding and Securing Device Vulnerabilities throughПодробнее

USENIX Security '21 - WaveGuard: Understanding and Mitigating Audio Adversarial ExamplesПодробнее

USENIX Security '21 - SLAP: Improving Physical Adversarial Examples with Short-Lived AdversarialПодробнее

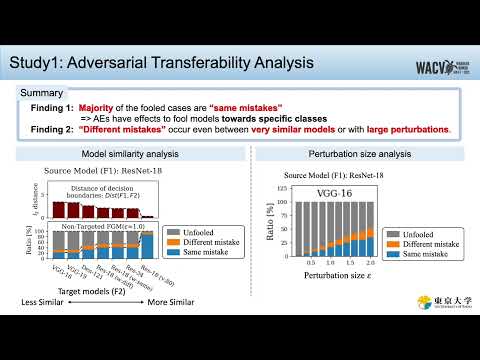
Closer Look at the Transferability of Adversarial Examples: How They Fool Different Models DifferenПодробнее
USENIX Security '18 - A4NT: Author Attribute Anonymity by Adversarial Training...Подробнее

Improving the Transferability of Adversarial Examples with New Iteration Framework and Input DropoutПодробнее

USENIX Security '24 - LaserAdv: Laser Adversarial Attacks on Speech Recognition SystemsПодробнее

USENIX Security '19 - ATTACK2VEC: Leveraging Temporal Word Embeddings to Understand theПодробнее

USENIX Security '23 - KENKU: Towards Efficient and Stealthy Black-box Adversarial Attacks against...Подробнее

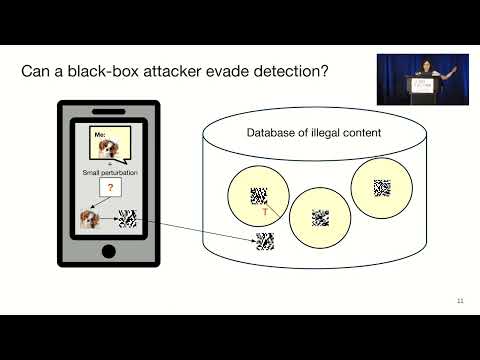
USENIX Security '22 - Adversarial Detection Avoidance Attacks: Evaluating the robustnessПодробнее
CVPR'23 - Sibling-Attack: Rethinking Transferable Adversarial Attacks Against Face RecognitionПодробнее

USENIX Security '20 - Hybrid Batch Attacks: Finding Black-box Adversarial Examples with LimitedПодробнее
