Joint Probability Density Functions and Bivariate Random Variables
The bivariate random variable (X,Y) jointly follow the probability density function f(x,y)=kx^2(8-y)Подробнее

Bivariate Continuous Random Variables |Probability and Statistics |Data Sc. & AI Lecture Video #160Подробнее
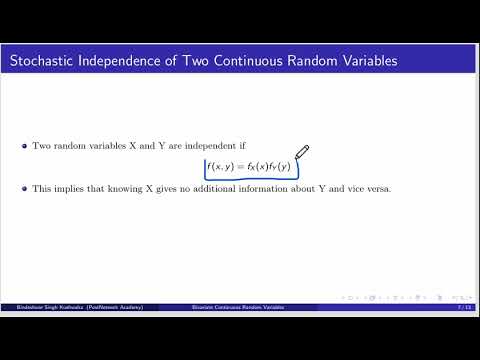
Multivariate Random VariablesПодробнее

Conditional Probability Mass FunctionПодробнее

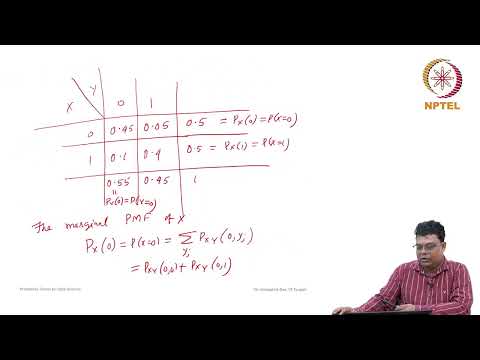
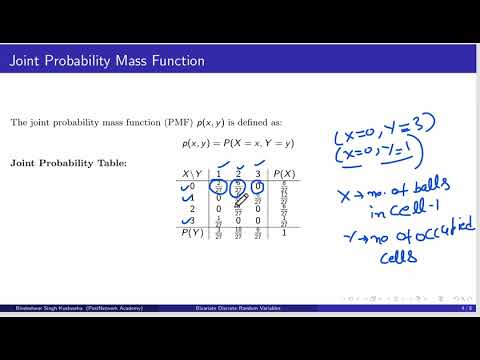
Joint Probability Mass Function, Marginal Probability Mass Function, ExamplesПодробнее

Numerical Examples on Moments for Bivariate Random VariablesПодробнее
Conditional Probability Density FunctionПодробнее
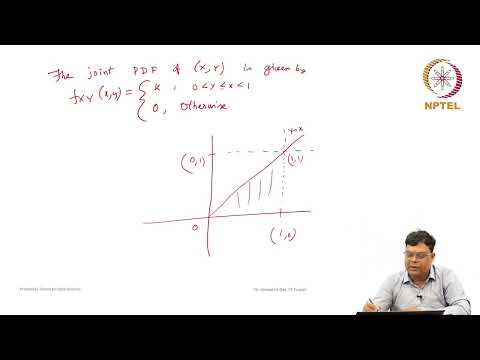
Numerical Examples on Probability Density FunctionПодробнее

Examples of Transformation of Bivariate Random VariablesПодробнее

Example of Bivariate Random VariableПодробнее

Examples of Transformation of Bivariate Random Variables #swayamprabha #ch38spПодробнее

Problem 2: Continuous Bivariate Problem Consider the continuous random variables X and Y that have …Подробнее
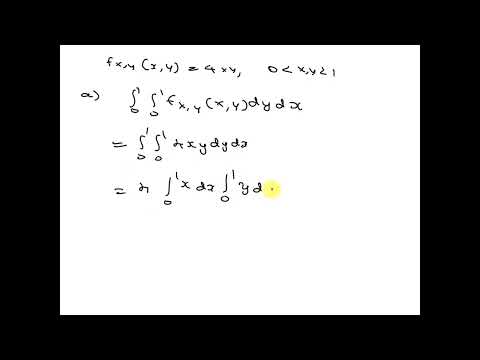
Example 2 Joint Probability Distribution Function for Continuous Random Variables-ProbabilityПодробнее
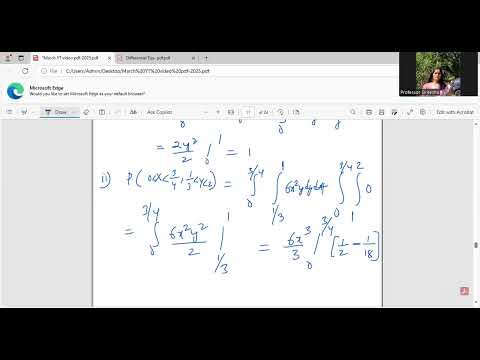
Bivariate Discrete Random Variables | Probability and Statistics | Video #158Подробнее
Properties of the Joint Cumulative Distribution Function of a Bivariate Random VariableПодробнее

Numerical Examples on Bivariate Discrete Random Variables and the Concept of Joint Probability.....Подробнее

ECE-340: L20 - Joint Random Variables (00:50:56)Подробнее

Episode 15 probability density function of random variable l independent l mathematical StatisticsПодробнее

Bivariate Discrete Cumulative Distribution Function | Probability and Statistics Video #159Подробнее

Examples of Joint Cumulative Distribution Functions, Marginals, and IndependenceПодробнее
